A Python simulation exploring a blockchain consensus mechanism leveraging quantum state fidelity, implemented using Qiskit. Nodes generate unique quantum states from candidate blocks, compare them via fidelity measurements, and reach consensus based on state similarity thresholding.
This project simulates a quantum-assisted blockchain consensus protocol using Qiskit. It explores the potential of quantum fidelity checks and entanglement-based randomness to enhance security and efficiency over classical Proof-of-Work mechanisms.
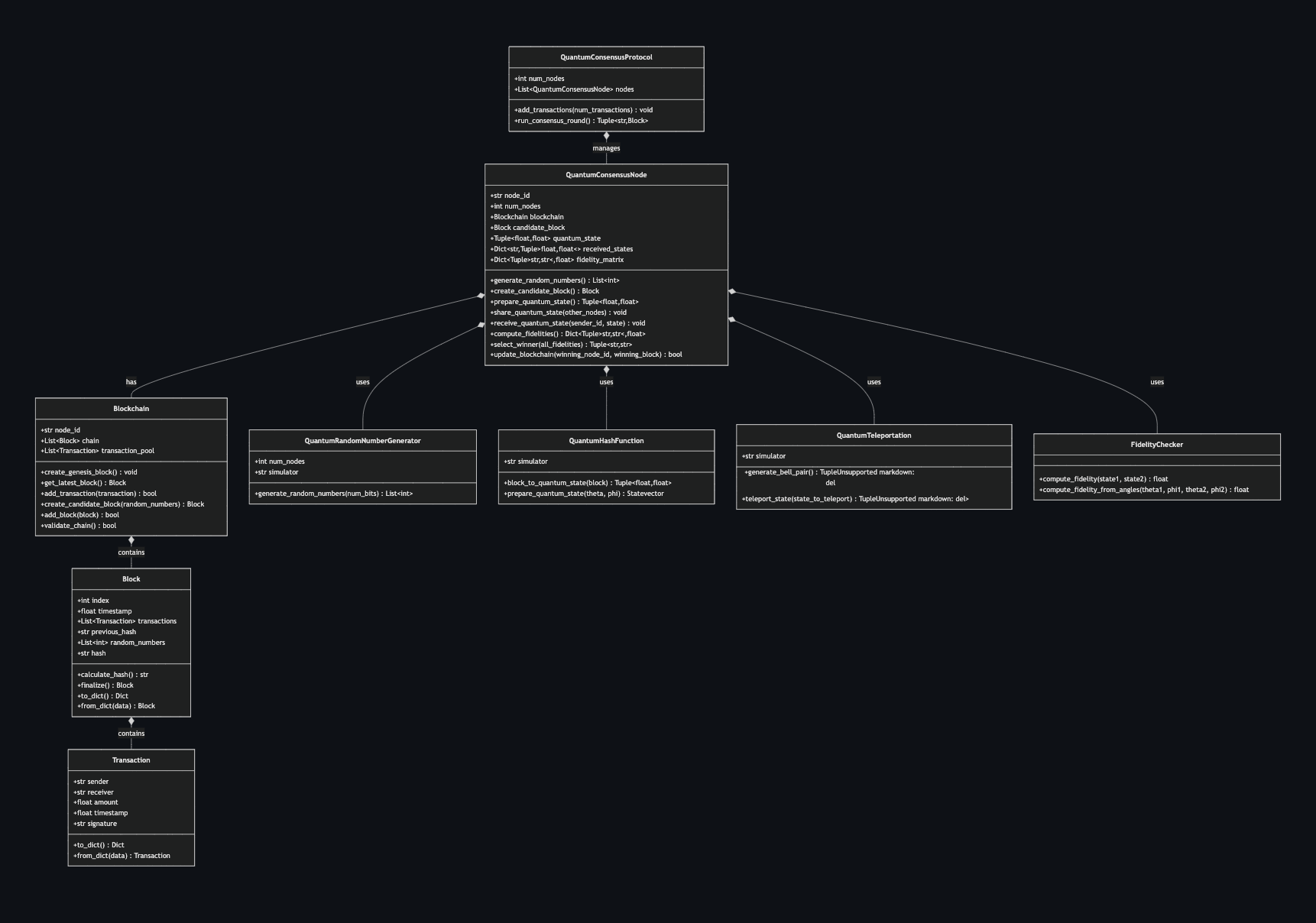

The simulation replaces classical proof-of-work with a mechanism where nodes propose blocks encoded as unique quantum states. Verification relies on measuring the similarity between these states.
We quantify the similarity between block states \(\rho\) and \(\sigma\) using fidelity:
\[ F(\rho, \sigma) = \left( \text{Tr} \sqrt{\sqrt{\rho} \sigma \sqrt{\rho}} \right)^2 \]
For pure states \( \lvert\psi_i\rangle \) and \( \lvert\psi_j\rangle \), this simplifies to \( F(\lvert\psi_i\rangle, \lvert\psi_j\rangle) = \bigl|\langle\psi_i|\psi_j\rangle\bigr|^2 \).
The Quantum Random Number Generator (QRNG) leverages GHZ states to produce correlated random bits:
\[ \lvert GHZ_N \rangle = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} (\lvert 0 \rangle^{\otimes N} + \lvert 1 \rangle^{\otimes N}) \]
Complex quantum circuits act as unitary operators \( U_{\text{block}} \) to map classical block data to a unique quantum state:
\[ \lvert\psi_{\text{block}}\rangle = U_{\text{block}} \lvert 0 \rangle^{\otimes n} \]
The system is a hybrid implementation combining a classical Python blockchain with quantum components simulated via Qiskit.
The protocol follows a multi-step process:
The simulation utilizes Qiskit Aer's statevector_simulator for ideal execution.